A Beginner’s Guide to OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) for EV Charging Operators
November 15, 2025As electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerates worldwide, EV charging infrastructure must evolve to handle higher demand, ensure reliability, and integrate with the smart grid. In this context the open, interoperable standard Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) becomes a backbone for communication between chargers and backend systems. When paired with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, OCPP-based charging networks can become smarter, more efficient, more secure and better for grid integration. This article explores how AI enhances OCPP-based EV charging networks, what benefits it brings, and what implementation considerations you should keep in mind.
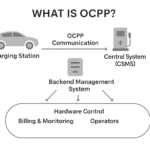
What is OCPP and Why It Matters
OCPP is an open communication protocol that allows EV charging stations (EVSEs) and charging station management systems (CSMS) to exchange data and commands. Key features of OCPP include remote start/stop, session data, firmware updates, smart charging and load management. Because it is vendor-neutral, it helps avoid lock-in and enables interoperability across different hardware and software ecosystems.
With OCPP as the foundation, charging network operators gain flexibility to upgrade, integrate new services (e.g., demand response, vehicle-to-grid) and expand their networks without being locked to one vendor.
Why AI is the Natural Partnership for OCPP
While OCPP provides the communications and data infrastructure, AI adds intelligence: the ability to anticipate, adapt and optimise. Some of the key reasons AI pairs well with OCPP-based networks include:
- Data rich environment: OCPP generates telemetry, session logs, charger state, user interactions and grid load data. AI thrives in data-rich settings.
- Dynamic demand and grid constraints: EV charging demand is inherently dynamic (time of day, user behaviour, tariff changes) and grid resources are constrained. AI can forecast, schedule and manage this complexity.
- Security and anomaly detection: Charging networks are connected infrastructure and vulnerable to faults or cyber-attacks. AI can detect anomalies in OCPP logs and charger behaviour in real time.
- Scalability: As networks grow, manual or rule-based control becomes unsustainable. AI enables automation and intelligent orchestration at scale.

Key Ways AI Enhances OCPP-Based EV Charging Networks
1. Load Forecasting and Demand Prediction
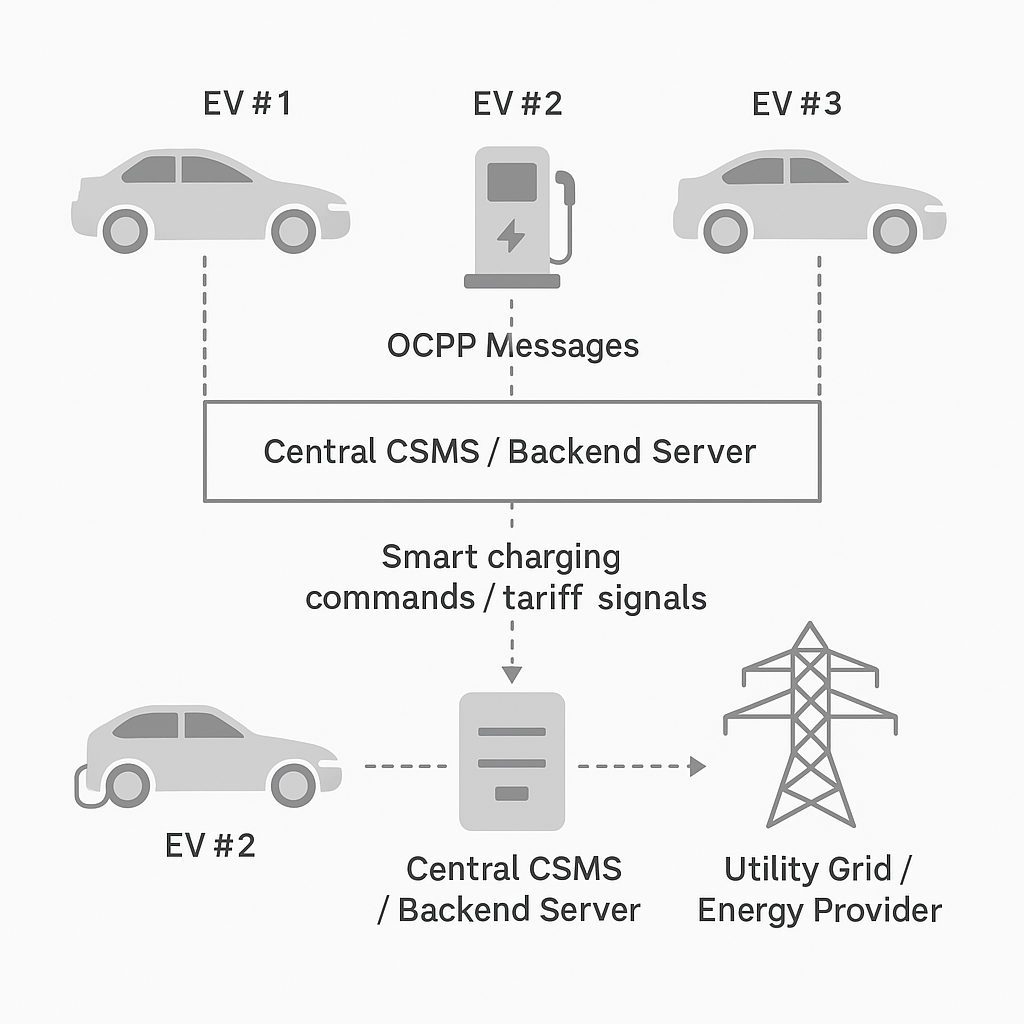
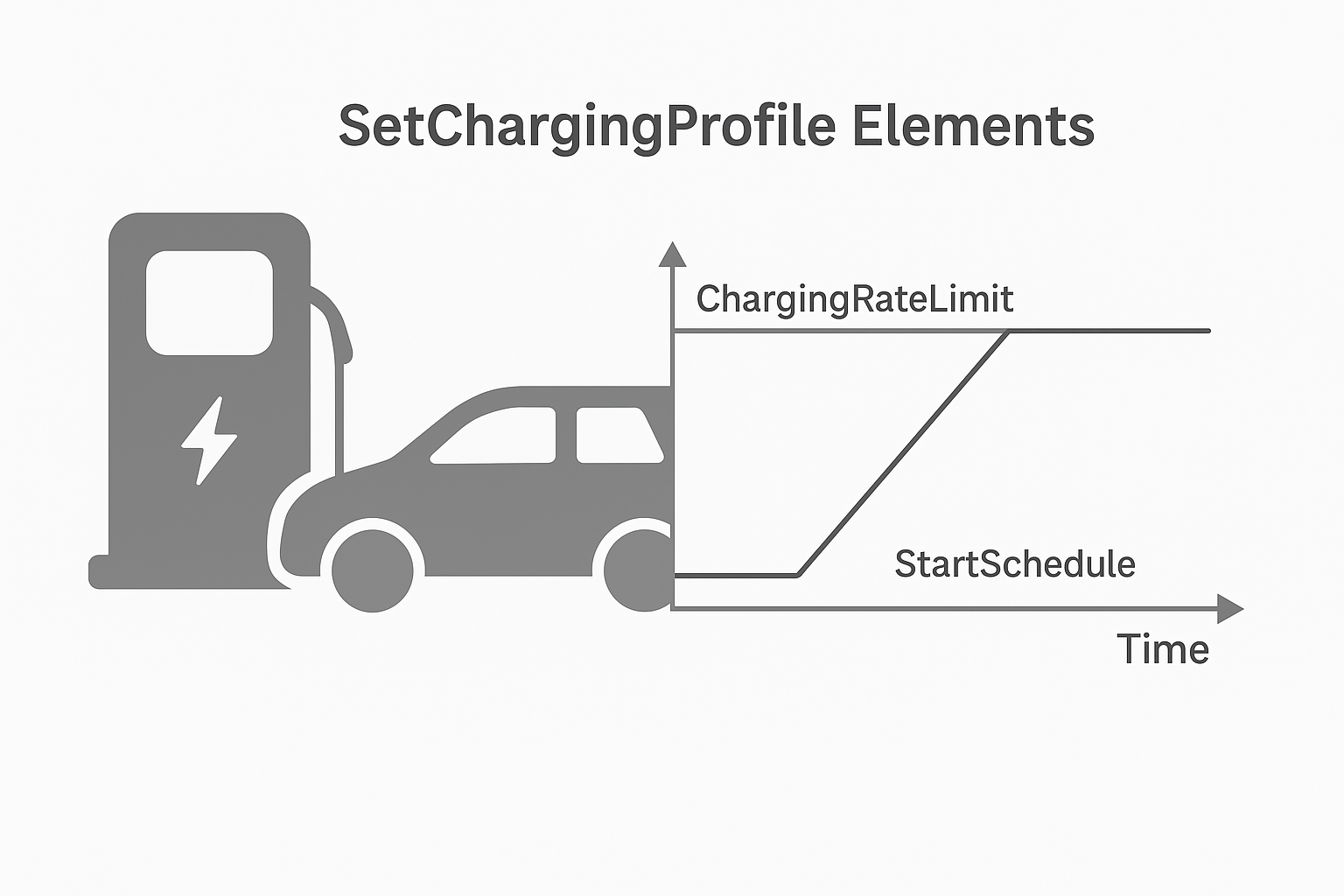
AI models (such as time-series forecasting, Prophet, XGBoost, LSTM/GRU) can predict the upcoming demand for charging sessions, aggregated station loads and feeder impacts. This helps operators to plan and set charging profiles in OCPP (e.g., via SetChargingProfile or GetCompositeSchedule commands) to avoid peaks and grid overload. For example, forecasting allows the charging system to anticipate high demand periods and allocate capacity accordingly.
By using OCPP telemetry and grid data, the AI forecast becomes the trigger for smart charging decisions.
2. Smart Scheduling and Load Balancing
Once demand is predicted, AI can schedule sessions, adjust charging rates or defer lower-priority sessions to manage loads effectively. This is especially important when multiple chargers share a feeder or in sites with limited connection capacity. Smart scheduling can be integrated via OCPP commands (for instance remote start/stop or charging profile changes).
The result: flatter load curves, improved utilisation, reduced cost of energy and fewer grid constraints.
3. Renewable & Tariff-Aware Charging
AI can optimise charging by considering external inputs such as time-of-use tariffs, renewable generation (solar/wind) and grid signals. In an OCPP-enabled network, the system can schedule charging during off-peak or high-renewable periods. One industrial blog notes how combining AI with OCPP enables “adaptive energy optimisation, adjusting charging profiles in response to real-time grid and pricing data.”
This aligns charging behaviour with sustainability goals and cost reduction.
4. Anomaly Detection & Predictive Maintenance
Charging stations and infrastructure can fail or may be subject to misuse, fraud or cyber-security threats. AI can continuously analyse OCPP logs and charger behaviour, detect outliers or suspicious patterns and trigger alerts or automated actions. For example, AI systems can detect charger faults before they result in downtime and schedule maintenance proactively.
This capability improves reliability, uptime and security of the charging network.
5. Real-Time Grid Integration & Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Support
As EVs become part of distributed energy resources (DER), AI-enabled OCPP networks can support bidirectional energy flows (V2G), dynamic pricing and grid services. Using AI to coordinate EVs, chargers and the grid opens possibilities such as demand response, frequency regulation and energy trading. The evolution of OCPP (e.g., version 2.1) and AI synergies make such advanced scenarios viable.
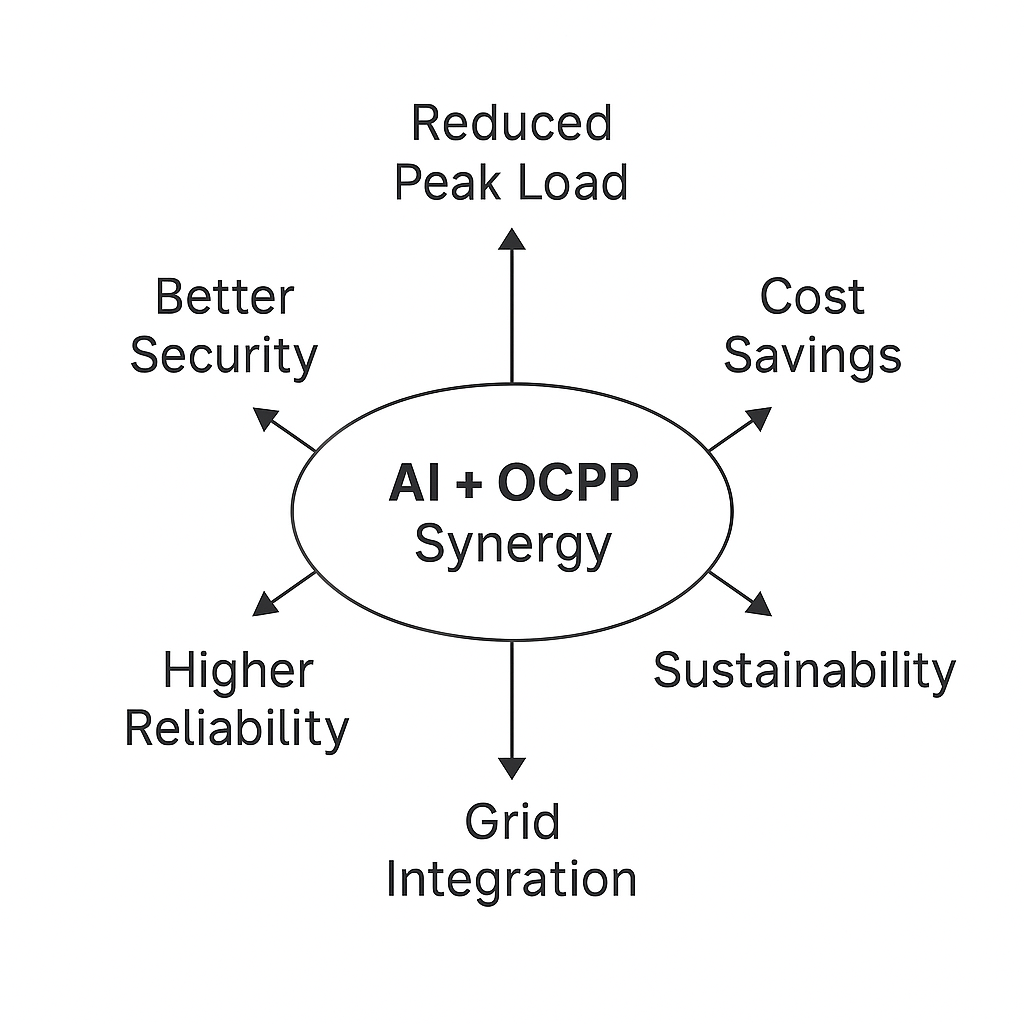
Benefits for Operators, Grid and EV Users
- Reduced operating cost: By forecasting and scheduling intelligently, operators can reduce demand charges, avoid peak energy premiums and optimise use of renewables.
- Improved reliability & user satisfaction: Less downtime, fewer charger faults and better user experience (through intelligent station choice, minimal wait times).
- Better grid impact: Flattened peaks, reduced stress, smoother feeder loads, improved integration with renewables.
- Security & compliance: Proactive anomaly detection, improved cybersecurity and standard-based interoperability (through OCPP).
- Scalability & future-proofing: An AI-enabled architecture makes it easier to scale networks, adopt V2G or DER services and integrate new business models.
Implementation Considerations & Best Practices
When deploying AI in an OCPP-based EV charging network, bear in mind:
- Data quality & volume: AI requires reliable, clean data from chargers, grid, user sessions and external signals. Ensure OCPP logs are captured and stored.
- Protocol version compatibility: Use a version of OCPP that supports the required commands and features (for example OCPP 2.0.1 with TLS for security) since newer features (V2G, DER) are supported.
- Edge vs-cloud architecture: For real-time decisions (e.g., anomaly detection) it may be preferred to have AI at the edge or near-station; for forecasting or scheduling, cloud may suffice.
- Privacy and security: AI models will deal with user session data and grid data—ensure encryption, certificate-based authentication and data governance (especially since OCPP networks are vulnerable).
- Integration with backend systems: The AI engine must integrate with the CSMS and issue proper OCPP messages (e.g., SetChargingProfile, ClearChargingProfile) to enforce decisions.
- Monitoring and feedback loop: Continuously monitor performance (peak reduction, cost savings, user metrics) and feed data back into AI models for improvement.
- Regulatory & grid-operator coordination: When engaging in demand response or V2G, ensure compliance with local grid regulations and coordination with utilities.
Real-World Example / Case Snapshot
In a recent study, an AI-integrated OCPP system achieved measurable improvements: using forecasting, scheduling and anomaly detection across a multi-station network, the researchers recorded significant reductions in feeder peak and charging cost, and high performance in anomaly detection.
This demonstrates that the combination of OCPP standard adherence and AI intelligence is not just theoretical—it delivers practical benefits.
Future Trends to Watch
- Agentic AI & autonomous control: AI agents will increasingly make autonomous decisions across charging networks, interacting with grid systems, EVs and users.
- Integration with distributed energy resources (DER) and V2G: EVs will act as grid assets, not just loads. AI + OCPP will enable smoother two-way energy flows.
- Federated learning & privacy-centric AI: As networks scale globally, federated AI allows models to train across sites without centralising sensitive data.
- Standard evolution (OCPP 2.1 and beyond): New protocol versions will support richer capabilities (DER, battery swapping, local cost calculation) and AI will leverage these features.
- Edge AI and digital twin integration: Charging stations may host on-site AI models or digital-twins of infrastructure for predictive maintenance and optimisation.
Conclusion
By combining the open, interoperable capabilities of OCPP with the predictive, adaptive power of AI, EV charging networks can evolve from reactive-and-manual to intelligent, efficient, scalable and resilient systems. Whether you run a single station or a large multi-site network, adopting AI-enhanced OCPP architecture offers real benefits in cost, reliability, grid integration and user satisfaction. As EV adoption grows, this synergy will be increasingly critical for smart cities, utilities and mobility operators alike.
